Montmorillonite-Zirconium Phosphate Catalysts for Methanol Dehydration
Authors
-
Hasanudin Hasanudin
*
 1
1
- Wan Ryan Asri 1, 2
- Qodria Utami Putri 1, 2
- Zainal Fanani 1, 2
-
David Bahrin
 3
3
-
Tuty Emilia Agustina
 3
3
-
Karna Wijaya
 4
4
Abstract
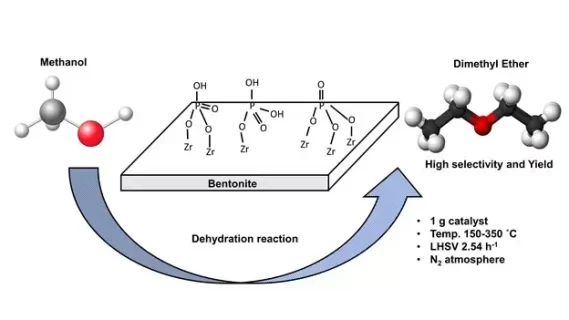
Modification of sodium montmorillonite was conducted using zirconium phosphate. The effect of a series of phosphate precursors such as dihydrogen phosphate, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, and sodium phosphate was observed. The catalyst was used in the conversion of methanol dimethyl ether using 1 g of catalyst at a temperature range of 150-350 ˚C with a Liquid Hourly Space Velocity (LHSV) monitored to 2.54 h−1 and N2 as carrier gas. The product was analyzed directly with a reactor system connected to gas chromatography. The X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscope-energy dispersive X-ray (SEM-EDX), N2 adsorption-desorption, and Temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia (NH3-TPD) were utilized to characterize the catalyst. The characterization showed that the modified sodium montmorillonite-zirconium phosphate was successfully synthesized. The study showed that modified montmorillonite using zirconium phosphate significantly increased the catalytic activity of sodium montmorillonite by providing medium and strong acid sites also increased the surface area. The modified sodium montmorillonite-zirconium phosphate from dihydrogen phosphate precursor exhibited the highest catalytic activity with the methanol conversion of 96.76%, dimethyl ether selectivity of 96.8%, and dimethyl ether yield of 93.67%, whereas the modified sodium montmorillonite-zirconium phosphate from diammonium hydrogen phosphate showed good stability towards methanol conversion.
Highlights
- Modified NaM using ZrP increased the catalytic activity towards methanol conversion
- The surface area of NaM increased after being modified by ZrP, promoted catalytic activity
- M-ZrP provided medium and strong acid catalytic active sites
- M-ZrP1 exhibited the highest catalytic activity than other modified NaM catalyst
- M-ZrP2 showed good stability toward methanol conversion