Doping TiO2 by Cr from tannery wastewater for improving its activity under visible light in the dye degradation
Authors
-
Endang Tri Wahyuni
*
 1, 2
1, 2
- Sri Wahyuni 1, 2
- Mandrea Nora 1, 2
-
Novianti Dwi Lestari
 1, 2
1, 2
- Suherman Suherman 1, 2
Abstract
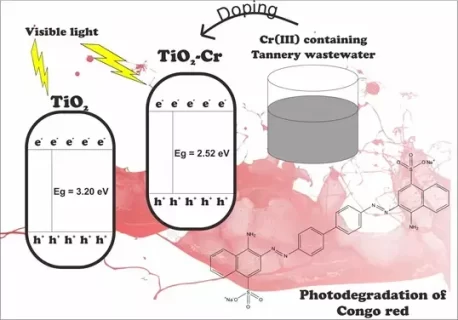
This paper deals with the comparison of the Cr (III) dopant from tannery wastewater to the Cr (III) from the pure salt solution on the character and activity of TiO2. The doping was conducted by hydrothermal method, and the Cr-doped TiO2 prepared was characterized by UV specular reflectance (SRUV), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray fluorescence instruments. The effect of the Cr (III) doping on the activity of the TiO2 was evaluated by Congo red photodegradation. The research results reveal that Cr (III) doping on TiO2 has been successfully reducing remarkably the band gap energy (Eg) from 3.13 eV to 2.64 eV, shifting into the visible region, and further noticeably improving TiO2 activity. The effect of the Cr (III) doping from the wastewater is found to be slightly higher than that of the salt solution. The highest degradation of 10 mg/L Congo red in 50 mL solution, can be reached by applying 30 mg of the photocatalyst in 60 mins and at pH 7.
Highlights
- A comparison of Cr-doped TiO2 activity from Cr(III) tannery wastewater and pure salt has been studied.
- Cr(III) doping on TiO2 reduce the band gap energy and improve TiO2 activity under visible light.
- The activity of TiO2-Cr from the wastewater was found to be slightly higher than that of pure salt.
- Hazardous tannery wastewater containing high Cr(III) concentration can be converted into useful material, such as dopan TiO2