Composting-vermicomposting of pigeon dropping waste. A contribution to the reduction of urban contamination
- Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico para la Industria Química (INTEC, UNL-CONICET), Ruta Nacional 168 Km 0, 3000 Santa Fe, Argentina and Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Católica de Santa Fe, Echagüe 7151, 3000 Santa Fe, Argentina
- Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico para la Industria Química (INTEC, UNL-CONICET), Ruta Nacional 168 Km 0, 3000 Santa Fe, Argentina
- Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico para la Industria Química (INTEC, UNL-CONICET), Ruta Nacional 168 Km 0, 3000 Santa Fe, Argentina and Departamento de Medioambiente (FICH-UNL), Ruta Nacional 168 Km 0, Ciudad Universitaria, 3000 Santa Fe, Argentina

Received: 2024-03-27
Revised: 2024-07-11
Accepted: 2024-12-16
Published in Issue 2025-06-01
Copyright (c) -1 Carolina Elisabet Masin, Alejandra Duran, Cristina Susana Zalazar, Maria Emilia Fernandez (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
PDF views: 213
Abstract
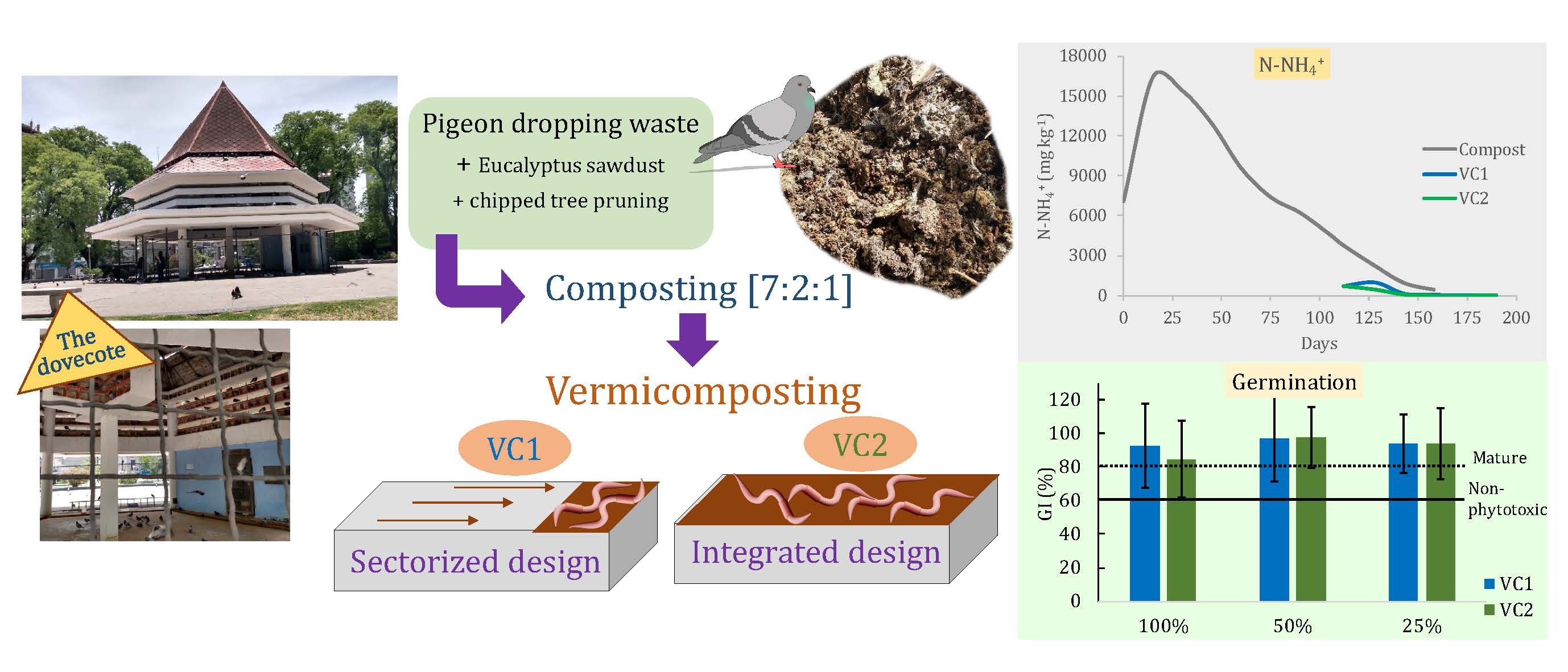
Purpose: Without a proper treatment, pigeon dropping waste (PDW) in the urban environment is a sanitary risk for the population because of nasty and irritating odors, a very high content of ammonium, and the presence of pathogens. This study deals with the recycling of PDW from a dovecote, situated in a public city plaza, to achieve its stabilization and eliminate sanitary risks.
Method: Composting of PDW with other locally available lignocellulosic residues (sawdust and chipped tree pruning) and vermicomposting employing Eisenia fetida earthworms was applied. Two designs were selected for the vermicomposting stage: (1) Sectorized, with a zone with earthworms and another zone of composted PDW with gradual incorporation to the first one and, (2) Integrated, consisting of the composted PDW, with E. fetida in the entire solid.
Results: The composting allowed a partial stabilization of the original mix of PDW, given its highly elevated initial content of ammonium (8693 mg kg-1). The combined processes almost eliminated the ammonium present (> 99% reduction) and the action of earthworms shortened the maturation time. Organic matter and electrical conductivity of the solids had important reductions. The treatment affected the resulting characteristics of the solids obtained but the germination index was above 80% in both cases.
Conclusions: Both designs allowed the obtention of two mature, non-phytotoxic vermicomposts. The sectorized vermicompost had better properties and had the advantage of being obtained with fewer initial number of earthworms.
Research Highlights
- Pigeon dropping waste was recycled by combined composting-vermicomposting process.
- Two vermicomposts were obtained by different sectorized and integrated designs.
- High ammonium content was reduced and nasty odors and pathogens were neutralized.
- Sectorized design produced a better vermicompost with fewer number of earthworms.
- Undiluted extracts of the vermicomposts rendered germination indexes over 80%.
Keywords
- Eisenia fetida,
- Pigeon waste,
- Ammonium,
- Phytotoxicity,
- Pathogen elimination
References
- AFNOR: Association française de normalisation (2005) Norme Française U44-051. Amendements organiques. Dénominations, spécifications et marquage. Cedex, France.
- Bernal MP, Alburquerque JA, Moral R (2009) Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour Technol 100:5444–5453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.11.027
- BOE: Boletin Oficial del Estado (2013) Real Decreto 506/2013 sobre productos fertilizantes. 164, 51119-51207. Oficial State Bulletin, Ministry of The Presidency, Spain
- Boruah T, Deka H (2023) Enumeration of synergistic relationship between carbon dioxide evaluation and nutrient budget during vermicomposting of cereal grain processing industry sludge. Bioresour Technol Rep 22:101418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2023.101418
- Bremner JM (1960) Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J Agric Sci 55:11–33. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600021572
- CCQC: California Compost Quality Council (2001) Compost Maturity Index, Technical Report. Nevada, CA, USA. 26 pp
- Dionisi CP, Mignone RA, Rubenacker AI, et al (2020) Monitoring of physicochemical parameters of soils after applying pig slurry. Analysis of its application in short and long periods in the province of Córdoba, Argentina. Microchem J 159:105545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105545
- Domínguez J, Gómez-Brandón M, Martínez-Cordeiro H, et al (2018) Bioconversion of Scotch broom into a high-quality organic fertilizer: Vermicomposting as a sustainable option. Waste Manage Res 36:1092-1099. https://doi:10.1177/0734242X18797176
- Gao M, Li B, Yu A, et al (2010) The effect of aeration rate on forced-aeration composting of chicken manure and sawdust. Bioresour Technol 101:1899–1903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.027
- Gao Y, Zhang C, Tan L, et al (2022) Full-Scale of a compost process using swine manure, human feces, and rice straw as feedstock. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.928032
- Gong X, Cai L, Li S, et al (2018) Bamboo biochar amendment improves the growth and reproduction of Eisenia fetida and the quality of green waste vermicompost. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 156:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.023
- Gutiérrez V, Gómez G, Rodríguez DC, et al (2023) Critical analysis of wastewater treatment using vermifilters: Operating parameters, wastewater quality, and greenhouse gas emissions. J Environ Chem Eng 11:109683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109683
- ISO 11268-2 (2023) Soil quality - Effects of pollutants on earthworms - Part 2: Determination of effects on reproduction of Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei and other earthworm species. International Organization for Standardization, 36 pp
- Jayakumar M, Emana AN, Subbaiya R, et al (2022) Detoxification of coir pith through refined vermicomposting engaging Eudrilus eugeniae. Chemosphere 291:132675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132675
- Laos F, Mazzarino MJ, Walter I, et al (2002) Composting of fish offal and biosolids in northwestern Patagonia. Bioresour Technol 81:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00150-X
- Leconte MC, Mazzarino MJ, Satti P, et al (2009) Co-composting rice hulls and/or sawdust with poultry manure in NE Argentina. Waste Manag 29:2446–2453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.04.006
- Lyu J, Park J, Kumar Pandey L, et al (2018) Testing the toxicity of metals, phenol, effluents, and receiving waters by root elongation in Lactuca sativa L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.006
- Ma L, Zhang L, Feng X (2024) Optimization of Eisenia fetida stocking density for biotransformation during green waste vermicomposting. Waste Manage 187:188-197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2024.07.016
- Maharjan KK, Noppradit P, Techato K (2023) Potential of Eisenia fetida (Redworm) for the conversion of three varieties of organic waste. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agricult 12:341-350. https://doi.org/10.30486/ijrowa.2022.1958871.1466
- Manu MK, Li D, Liwen L, et al (2021) A review on nitrogen dynamics and mitigation strategies of food waste digestate composting. Bioresour Technol 334:125032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125032
- Masin CE, Fernandez ME, Lescano MR, Zalazar CS (2020) Bioconversion of agro-industrial wastes: Combined compost and vermicompost processes using Eisenia fetida for stabilization of poultry litter. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agricult 9:107–118. https://doi.org/10.30486/IJROWA.2020.1885790.1011
- Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
- Nagannawar MF, Patil SR, Biradar PM (2021) Growth and reproduction of the epigeic earthworm, Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826) cultured in various organic wastes. J Adv Zool 42:43–59. https://doi.org/10.17762/jaz.v42i01.5
- Niedzialkoski RK, Marostica R, Damaceno FM, et al (2021) Combination of biological processes for agro-industrial poultry waste management: Effects on vermicomposting and anaerobic digestion. J Environ Manage 297:113127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113127
- Nobili S, Masin CE, Zalazar CS, Lescano MR (2022) Bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil using local organic materials and earthworms. Environ Pollut 314:120169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120169
- Nobili S, Masin CE, Zalazar CS, Lescano MR (2024) Vermistabilization of excess sludge employing Eisenia fetida: Earthworm histopathological alterations and phytotoxicity evaluation. J Environ Manage 368:122174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122174
- Onwosi CO, Igbokwe VC, Odimba JN, et al (2017) Composting technology in waste stabilization: On the methods, challenges and future prospects. J Environ Manage 190:140–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.051
- Pizarro MD, Céccoli G, Muñoz FF, et al (2019) Use of raw and composted poultry litter in lettuce produced under field conditions: microbiological quality and safety assessment. Poult Sci 98:2608–2614. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez005
- Rodrigues de Oliveira GA, Morais Leme D, de Lapuente J, et al (2018) A test battery for assessing the ecotoxic effects of textile dyes. Chem Biol Interact 291:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.06.026
- SCyMA, SENASA (2019) Anexo I: Marco Normativo Para La Producción, Registro y Aplicación De Compost. https://www.argentina.gob.ar/normativa/nacional/resolución-1-2019-318692/texto. Accessed 10 Nov 2023
- Sharma D, Prasad R, Patel B, Parashar CK (2022) Biotransformation of sludges from dairy and sugarcane industries through vermicomposting using the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agricult 11:165–175. https://doi.org/10.30486/IJROWA.2021.1922034.1196
- Sharma K, Garg VK (2017a) Management of food and vegetable processing waste spiked with buffalo waste using earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:7829–7836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8438-2
- Sharma K, Garg VK (2017b) Vermi-modification of ruminant excreta using Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19938–19945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9673-2
- Singh S, Singh J, Kaur A, et al (2019) Nutrient recovery from pigeon dropping by using exotic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Sustain Chem Pharm 12:100126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2019.01.003
- Song B, Manu MK, Li D, et al (2021) Food waste digestate composting: Feedstock optimization with sawdust and mature compost. Bioresour Technol 341:125759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125759
- Srivastava PK, Singh A, Kumari S, et al (2023) Production and characterization of sustainable vermimanure derived from poultry litter and rice straw using tiger worm Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 369:128377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128377
- Swati A, Hait S (2018) A Comprehensive review of the fate of pathogens during vermicomposting of organic wastes. J Environ Qual 47:16–29. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2017.07.0265
- Thomson A, Price GW, Arnold P, et al (2022) Review of the potential for recycling CO2 from organic waste composting into plant production under controlled environment agriculture. J Cleaner Prod 333: 130051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130051
- Tognetti C, Laos F, Mazzarino MJ, Hernández MT (2005) Composting vs. vermicomposting: A comparison of end product quality. Compost Sci Util 13:6–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657X.2005.10702212
- USEPA (2003) EPA/625/R-92/013. Control of Pathogens and Vector Attraction in Sewage Sludge. United States Environmental Protection Agency, 177 pp
- USEPA (1996) Ecological Effects Test Guidelines: Seed Germination/Root Elongation Toxicity Test. United States Environmental Protection Agency, 8 pp
- USEPA (1993) 40 CFR Part 257, 403 and 503 Standards for Use or Disposal of Sewage Sludge. US Government Printing Office Fed Regist 58: 9248–9415
- Villa-Serrano AM, Perez-Murcia MD, Perez-Espinosa A, et al (2010) Characterization and Agronomic Use of pigeon manure: a case study in the Northeast Transmontano Region (Portugal). 14th Ramiran International Conference: Treatment and use of organic residues in agriculture: Challenges and opportunities towars sustainable management, ISBN: 978-972-8669-47-8. 4 pp. Lisbon, Portugal
- Villar I, Alves D, Mato S (2017) Product quality and microbial dynamics during vermicomposting and maturation of compost from pig manure. Waste Manage 69:498–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.031
- Woods E, Rondon Berrio V, Qiu Y, et al (2024) Biomass composting with gaseous carbon dioxide capture. RSC Sustainability 2: 621. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3su00411b
- Yuvaraj A, Thangaraj R, Ravindran B, et al (2021) Centrality of cattle solid wastes in vermicomposting technology – A cleaner resource recovery and biowaste recycling option for agricultural and environmental sustainability. Environ Pollut 268:115688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115688
- Zucconi F, Monaco A, Forte M, Bertoldi MD (1985) Phytotoxins during the stabilization of organic matter. In: Gasser JKR (ed.), Composting of agricultural and other wastes. Elsevier Applied Science Publication, New York, pp. 73–86

 10.57647/ijrowa-bg19-nr15
10.57647/ijrowa-bg19-nr15