Nitrogen-enriched liquid organic fertilizers (LOFs) production for sustainable agriculture: A review
- Department of Biosystems Technology, Faculty of Technology, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Pitipana, Homagama, Sri Lanka
- Department of Civil and Environmental Technology, Faculty of Technology, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Pitipana, Homagama, Sri Lanka
- Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Galaha Road, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
- Department of Plant, Food and Environmental Sciences, Faculty of Agriculture, Dalhousie University, Truro, Nova Scotia, B2N 5E3, Canada

Received: 2023-07-26
Revised: 2023-10-17
Accepted: 2024-01-17
Published in Issue 2024-04-04
Copyright (c) 2024 @Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
PDF views: 562
HTML views: 38
Abstract
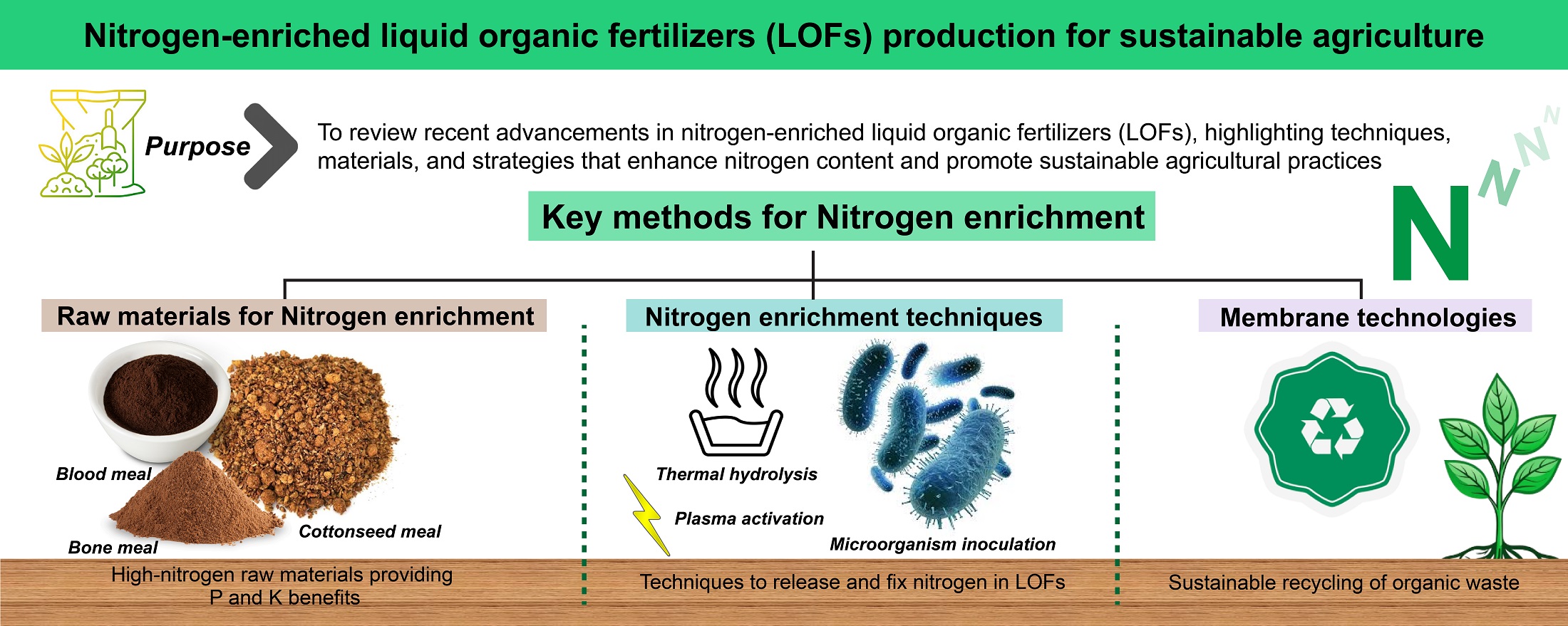
Purpose: Although the popularity of liquid organic fertilizers (LOFs) has considerably increased recently, there have been concerns over their usage due to low nitrogen content. This study aims to discuss the current developments in nitrogen-enriched LOFs that address the above limitation, subsequently promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Method: A thorough review of existing literature on nitrogen-enriched LOFs based on their chemical attributes and methodologies to increase the nitrogen content.
Results: The research highlights several promising methods for nitrogen enrichment, such as using high-nitrogen raw materials like cottonseed meal, bone meal, and blood meal, which also provide phosphorus and potassium benefits. Also, techniques like thermal hydrolysis, plasma activation, and inoculation of microorganisms can release and fix nitrogen in LOFs. Membrane technologies promise sustainably by recycling organic waste. Combining these materials and processes results in well-balanced nutrient profiles and improve the agricultural value of LOFs. However, formulating nitrogen-enriched LOFs requires considering critical factors like organic carbon content, pH values, raw material availability, cost implications, and overall sustainability. Optimizing these factors potentially lead to eco-friendly solutions for sustainable agriculture.
Conclusion: Cost-effective nitrogen enrichment in LOFs can be achieved through diverse methods and raw materials. Future investigations should focus on discovering raw materials with high nitrogen content, devising innovative enrichment techniques, and rigorously evaluating the efficacy of fertilizers. Investments in research, development, distribution, storage, packaging, and value-addition processes are essential to bolster LOF production and enhance affordability and accessibility, thus fostering sustainable agricultural practices.
Keywords
- Liquid organic fertilizers (LOFs),
- Membrane techniques,
- Nitrogen-enrichment,
- Nitrogen-fixing microorganisms,
- Plasma activation,
- Sustainable agriculture

 10.57647/ijrowa-txen-q116
10.57647/ijrowa-txen-q116