
The concept of the volume is to survey all the key geoparks throughout Europe in terms of their palaeontological significance. The first 25 articles in this Part cover the long span of geological time from the Precambrian to the Permian, arranged in chronostratigraphic order. These document some of the most important early stages in the […]
Together, places of scientific, historical or cultural significance within a region and the artefacts uncovered therefrom and displayed in museums and collections make up the total heritage of the region in question. Seemingly lifeless places and objects become enlivened in UNESCO geoparks through the combined efforts– geared towards education and tourism – of managers, researchers […]

The North West Highlands Geopark is probably one of the largest geoparks anywhere, comprising 2000 km2 of remote, mountainous and coastal terrain. It was the first European Geopark to be recognised in Scotland in 2004 and was designated by UNESCO as a Global Geopark in 2015. Since then, it has been very successful in delivering […]
Across the Ediacaran to Cambrian transition, some 541 Ma, the Earth’s biosphere changed from one dominated by microbial organisms to one where multicellular organisms, including animals, rose to importance. Within a few tens of millions of years into the Cambrian Period an array of animal groups appeared, some extinct and others ancestral to modern groups, […]

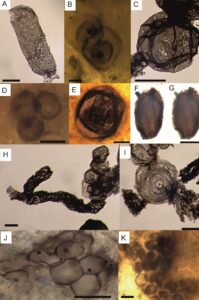
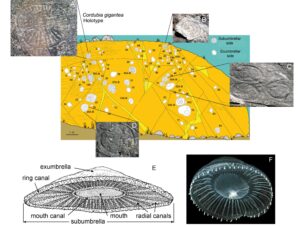
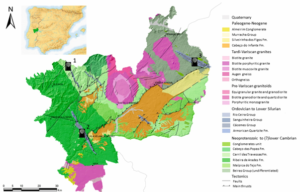
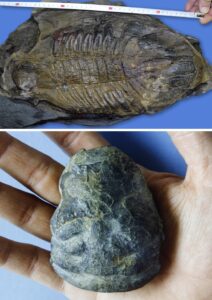
Some exceptional paleontological trilobite sites located in the Sierra Norte de Sevilla UNESCO Global Geopark are presented herein, together with an analysis of their geotourism / geotrail potential and a proposal for geoconservation. The sites are of Marianian age, a regional stage and age of the Cambrian Mediterranean Subprovince which was defined within the territory […]

Early Cambrian fossils sites of two Natural Monuments of the Sierra Norte de Sevilla Geopark are highlighted. The first of these shows archaeocyath and stromatolite bioconstructions at the Cerro del Hierro site, one of the most complete and best exposed in the European Cambrian record. The other exceptional setting is the Constantina site, which preserves […]
The Spanish Courel Mountains UNESCO Global Geopark has strong educational and touristic resources despite limited preservation of Paleozoic invertebrate fossil assemblages within metamorphic rocks. The paleontological sites are managed by means of their inventory and integration in a Geographical Information System, the construction of virtual 3D fossil models, the creation of a fossil collection exhibition, […]

Penha Garcia Ichnological Park is the most important fossil site and one of the most significant geosites of international relevance, in the territory of Naturtejo UNESCO Global Geopark. This municipal protected area is a key site for the study of trace fossil diversity at high paleolatitudes in the early stages of the Great Ordovician Biodiversification […]

The Early Paleozoic oceans were generally characterized by short trophic chains and simple ecological tiering dominated by suspension-feeding organisms. However, the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event (GOBE) was responsible for the complexification of food webs, increasing depth and diversity of substrate ecospace utilization and increasing benthic competition for resources near the water-substrate interface. Daedalus is an […]

Middle Ordovician successions occur at Naturtejo UNESCO Global Geopark in five Variscan-folded, kilometer- to tens of kilometer-long structures. Four of them revealed to be fossiliferous in the different recognized lithostratigraphic units, middle-to-uppermost Darriwilian in age, with particular emphasis for Brejo Fundeiro (Oretanian regional chronostratigraphic stage) and Fonte da Horta (Dobrotivian regional stage) formations. Recent paleontological […]

Naturtejo UNESCO Global Geopark (Portugal) area includes deposits from the Neoproterozoic to the Quaternary. Despite its limited exposure area in major Variscan folded structures, the Ordovician series hosts some of its most famous geological heritage features, such as the Penha Garcia Ichnological Park. The Upper Ordovician of the Central Iberian Zone is still far from […]
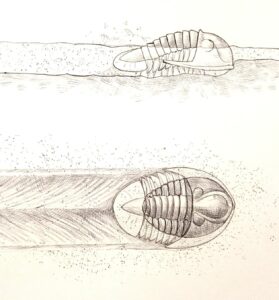
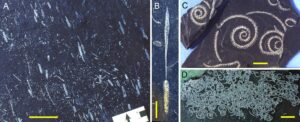
Cruziana is a common and widespread trace fossil in Lower Palaeozoic strata that is generally attributed to the activity of trilobites. The Lower to Middle Ordovician Armorican Quartzite Formation of southern Europe contains well-preserved examples of the Cruziana rugosa Group. This paper outlines how Cruziana forms an important part of the geological heritage in the […]
The giant Ordovician trilobites from the Canelas quarry constitute the most iconic sign of identity of the Arouca UNESCO Global Geopark at an international level. Palaeontological studies determined the importance of this fossil locality for studying aspects of the social behavior of these marine arthropods and their interactions with other represented invertebrate fossil groups. Although […]
The Paleozoic succession of the Sierra Norte de Sevilla UNESCO Global Geopark (Ossa Morena Zone of the Iberian Massif, SW Spain) includes a nearly complete Silurian succession, ca. 150 m thick, deposited in an outer shelf setting. In the core part of the Valle syncline, the El Pintado-1 section exhibits a condensed graptolite-rich Silurian black-shale […]
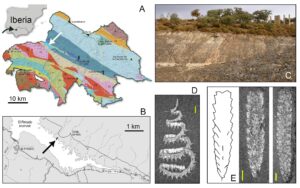
The Paleozoic succession in the Nevera inlier of the Molina-Alto Tajo UNESCO Global Geopark (Western Iberian Cordillera, NE Spain) includes an incomplete, richly fossiliferous Silurian succession, ca. 350‒400 m thick, at the locality of Checa, one of the geosites of international interest in the Paleozoic of Spain. The Checa section starts with quartzites (Los Puertos […]
The Black Country UNESCO Global Geopark, located in central England, joined the Global Geopark Network in July 2020. It is the most urban Geopark in the network with a population of approximately 1.1 million people. Located in an area rich in raw materials (Carboniferous coal, iron, and clay; Silurian limestone), it was quarried and mined […]

Shetland UNESCO Global Geopark encompasses a wide variety of well-exposed and accessible geological features. The combination of ocean floor remnants on top of ancient continental crust, a cross-section through a volcano, and evidence of earth movements is preserved nowhere else in the world and, individually, are some of the best examples known. Devonian rocks deposited […]

The coral-rich limestones of the English Riviera UNESCO Global Geopark were an important component of the original definition of the Devonian System, introduced by Sedgwick and Murchison in 1840. They are, therefore, both a local highlight of the geological succession but have an important position within the history of geology. Formed in the tropical seas […]

This paper introduces the Middle Devonian trilobites of Gerolstein, found on the famous trilobite fields of Gees and at the Auberg hill in Gerolstein. The research history and local geology of both sites are briefly discussed and key publications for further studies are provided. Owing to the early start of trilobite related research in the […]

The Viar Basin, the largest of the Carboniferous basins in the Sierra Norte de Sevilla UNESCO Global Geopark, has yielded an important fossil flora. The flora is important stratigraphically and paleoecologically, and the collection sites have significant heritage value as they were studied by eminent geologists of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. The […]

Piesberg quarry is famous for its Upper Carboniferous plant and arthropod fossils, including several holotypes of flying insects. The high degree of maturity of the Piesberg strata, such as the presence of anthracitic coal, quartzite, and large quartz crystals, led to controversies over a possible underlying thermal anomaly. The Piesberg is of further importance for […]

The late Paleozoic deposits in several basins of the Bohemian Massif are well known for their rich abundance of petrified tree trunks. The area of the UNESCO Global Geopark Bohemian Paradise includes a substantial part of one of the largest ones, the Krkonoše Piedmont Basin. Deposits of this basin contain the most complete fossil record […]

Carboniferous fossils from the Burren and Cliffs of Moher UNESCO Global Geopark, County Clare, Ireland are rated by their promotional potential in the form of celebrity A, B or C-listings. Trace fossils, crinoids, brachiopods, corals and vertebrates are the most exposed to public view at a number of high-profile visitor locations and the relative risk […]

The Permian breccias, conglomerates and sandstones of the English Riviera UNESCO Global geopark were deposited in quite harsh, desert environments just north of the Permian Equator. Body fossil evidence is completely lacking but rare trace fossils provide evidence of a land-based community. There is a variety of traces present, probably indicative of the presence of […]

The Fossil Forest of the Aragoncillo Range is one of several paleontological sites of exceptional scientific value in the Sierra de Selas (Province of Guadalajara, central Spain). This shows an accumulation of silicified tree trunks along with well-preserved macro- and microflora of lower Permian age. This ancient forest, dominated by tree ferns and conifers, was […]

The iconic Kupferschiefer is a stratigraphic marker horizon of the Upper Permian in Northern and Central Europe, which is recognized internationally as a unique stratum because of its outstanding preservation of fish, reptile, and plant fossils. In the UNESCO Global Geopark TERRA.vita, Kupferschiefer fossils have been found at three tectonically uplifted elevations: Hüggel, Schafberg, and […]
