Investigation on the Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities of Green synthesized Cupric Oxide Nanoparticles using Clitoria ternatea
Authors
-
S. Prabhu
*
 1, 2
1, 2
-
T. Daniel Thangadurai
 3
3
-
P. Vijai Bharathy
 4
4
-
Pon Kalugasalam
 5
5
Abstract
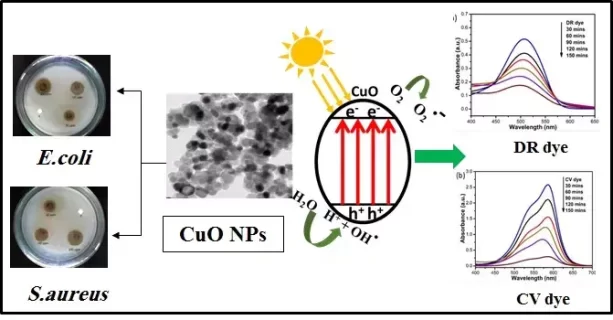
Green synthesis of cupric oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) has been promoted as an environmentally-friendly, cost-effective and high yield method. The CuO NPs have been synthesized by reducing copper sulphate using an aqueous flower extract of Clitoria ternatea. The UV-visible peak observed at 251 nm confirmed the formation of CuO NPs. The optical bandgap energy value of CuO NPs was found to be 2.16 eV. The presence of Cu-O band at 490 cm−1 in the FTIR spectrum confirms the formation of the CuO NPs. The XRD exhibits monoclinic structure with an average crystallite size of 17.46 nm. The negative zeta potential value (-17.7 mV) demonstrated the stability of CuO NPs. The formation of agglomerated and roughly spherical NPS was shown by FESEM images. As seen in the HRTEM images, the nanostructure appears to be aggregated CuO NPs, and the average size of the particle was found to be 18 nm that matched with the XRD analysis. The EDX analysis showed presence of Cu (96.19%) and O (3.81%) in the spectrum. The CuO NPs exhibit significant antibacterial activity against Gram +Ve Staphylococcus aureus and Gram –Ve Escherichia coli bacteria. Finally, the synthesized CuO nanostructures demonstrate the photocatalytic degradation of Direct Red (DR) and Crystal Violet (CV) dyes under sunlight. The efficiency of degradation within 150 min was determined to be 65% and 88.3%, respectively for DR and CV. This effective removal method under sunlight may support a cost-effective method for degradation of DR and CV dyes from wastewater.
Highlights
- Clitoria ternatea flower extract was used for the first time to synthesize CuO NPs.
- The flower extract serves as a strong reducing and capping agent.
- The CuO NPs have an average particle size of 18 nm, with roughly spherical shape.
- The CuO NPs exhibit better resistance against coli bacteria.
- The CuO NPs exhibit significant catalytic activities against CV dye (88.3%) compared with that against DR dye (65%).