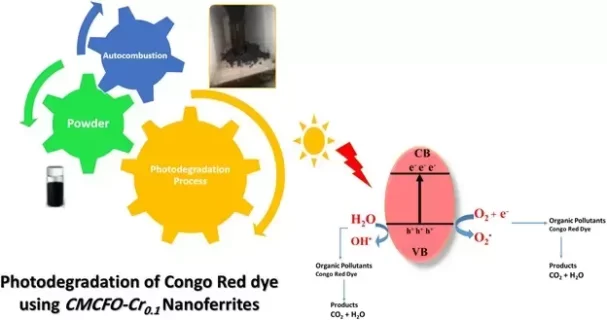
CMCFO-Cr0.1 Nanoferrites: Sol-gel Synthesis, Structural, and Magnetic Studies: Applications for Photodegradation of Congo Red Dye
Authors
- Ahmed Selmi 1
- Hakimeh Teymourinia 2, 3, 4
-
Armin Zarei
 4
4
- Mohamed Timoumi 5
- Ali Ramazani * 2, 4
Abstract
One of the foremost inescapable impediments that industrial sectors face is to remove organic pollutants, which affected nature and threatened the existence of species per se. Nanoscale magnetic ferrites are considerable materials for removing the majority of organic dyes due to their unique properties and high potential photocatalytic activity. Their photocatalytic performance in semiconductor nanocrystals has also received many enthusiasts over the last couple of years. Changing nanoferrites’ architectural building blocks and increasing their bandgap energy may improve their photocatalytic peculiarities. In the present investigation, we have studied nanoscale magnetic ferrites with Co0.4Mg0.4Cu0.2Fe1.9Cr0.1O4, (CMCFO-Crx, x= 0.1) formula. CMCFO-Crx has synthesized via sol- gel approach. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by XRD, SEM, UV-vis analysis, and magnetic measurement, revealing the cubic spinel structure with space group Fd-3m (N° 277), average size between 20 and 60 nm, higher bandgap energy and saturation magnetization (446 emu/g) in the presence of transition metals. The results demonstrated in CMCFO-Crx (x=0.1) compound, the Curie temperature decreases to 446 K by the substitution of Fe3+ by Cr3+ ions. The synthesized powder nanoferrites efficiently degraded the Congo Red (CR) dye (84 %) under UV irradiation, for which the most probable degradation pathway is proposed. The recyclability test exhibited the nanoscale magnetic ferrites catalysts are sensibly efficient, stable, and facile recoverable by an external magnet. Thus, the CMCFO-Crx compounds can be an applicable catalyst in wastewater treatment.
Highlights
- CMCFO-Cr1 Nanoferrites synthesized through simple and facile Sol-gel technique.
- Synthetic Nanoferrites were characterized by XRD.
- Magnetic peculiarities of the Nanoferrites were investigated.
- The prepared Nanoferrites were applied for photodegradation of Congo Red Dye.
- The effects of various factors such as Effect of light, Influence of catalyst dose, and Influence of irradiation time onphotocatalytic activities of these Nanoferrites were comprehensively investigated.