Antibacterial activity of the Iron-Zinc Oxide nanoparticles synthesized via electric discharge method
Authors
Abstract
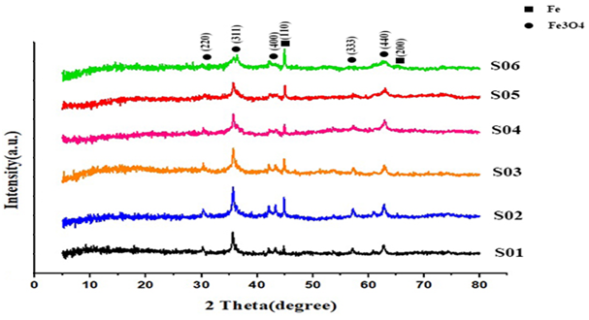
Recently, with the increase in diseases caused by bacterial and viral infections, the need for antibacterial agents has widely increased. On the other hand, with the development of drug resistance to organic groups of antibiotics, new antibiotics have attracted the attention of researchers because new methods are needed to reduce the activity of bacteria. Nanotechnology is increasingly being used for medical applications and is useful as an approach to kill or reduce the activity of various microorganisms. Metal oxides are considered for medical applications, especially as antibacterial agents, due to their potential advantages and suitable nanoscale properties. In this study, the electric discharge method was employed for the preparation of the iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) and iron-zinc oxide nanoparticles (IZONPs). As the IONPs and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZONPs) attack various gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria by different mechanisms, it seems that the simultaneous use of these oxides can effectively kill various bacteria in outdoor and indoor media. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized via XRD, UV-Visible, FE-SEM, EDS, HR-TEM, and TEM techniques. The obtained results showed that the IZONPs with mean particles size between 11 and 33 nanometers have successfully been synthesized in various experimental conditions. Also, the antibacterial properties of these nanoparticles were evaluated and the particles showed antibacterial properties against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
References
1. Bhushan M., Kumar Y., Latha P., Vismanath A., (2018), Facile synthesis of Fe/Zn oxide nanocomposites and study of their structural, magnetic, thermal, antibacterial and cytotoxic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 209: 233-248.
2. Lewis K., (2013), Platforms for antibiotic discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 12: 371-387.
3. Aminov R. I., (2009), The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Environ. Microbiol. 11: 2970-2988.
4. Shahriyari F., Yarali D., Ahmadi R., Shabir H., Wei W., (2020), Synthesis and characterization of Cu-Sn oxides nanoparticles via wire explosion method with surfactants, evaluation of in-vitro cytotoxic and antibacterial properties. Adv. Powder Tech. 31: 2337-2347.
5. Mohammad J. H., Katharina M. F., Ashkarran A., Dorleta J., Idoia R., Teofilo R., Vahid S., Wolfgang J. P., Mahmoudi M., (2012), Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends. Biotechnol. 2012. 30: 499-511.
6. Slavica S., Sneha S., Franica H., Vidic J., (2016), Pure and multi metal oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial and cytotoxic properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 14: 1-20.
7. Lemire J., Harrison J., Turner R., (2013), Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11: 371-384.
8. Zhang W., Shi X., Jing H., Zhang Y., Wu Z., Xian Y., (2012), Bacitracin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity. Chem. Physic. Chem. 13: 3388-3396.
9. Buzuayehu A., Enyew A., Aschalew T., Ananda H. C., (2020), A review on enhancing the antibacterial activity of ZnO: Mechanisms and microscopic investigation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 15: 1-19.
10. Buzuayehu A., Ananda H. C., Enyew A., Yeshaneh A., (2020), PVA assisted ZnO based mesoporous ternary metal oxides nanomaterials: Synthesis, optimization, and evaluation of antibacterial activity. Mater. Res. Express. 7: 1-13.
11. Lu A., Salabas E. L., Schüth F., (2007), Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 46: 1222-1244.
12. Nazari M., Ghasemi N., Madaah H., Mousavi M., (2014), Synthesis and characterization of maghemite nanopowders by chemical precipitation method. J. Nanostructure Chem. 4: 1-5.
13. Sadeghi B., Jamali M., Kia Sh., Amini Nia A., Ghafari S., (2010), Synthesis and characterization of Silver nanoparticles for antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 1: 119-124.
14. Sadeghi B., Mohammadzadeh M., Babakhani B., (2015), Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Stevia rebaudiana leaf extracts: Characterization and their stability. J. Photoch. Photobio B. 148: 101-1016.
15. Sadeghi B., Gholamhoseinpour F., (2015), A study on the stability and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ziziphora tenuior (Zt) extract at room temperature. Spectrochim. Acta A. 134: 310-315.
16. Sintayehu T. G., Gemechis A. M., Ananda H. C., Endale T. M., Ravikumar C. R., Bedasa A. G., Fedlu K. S., (2022), Biogenic synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using leaf extract of Thymus schimperi and application for removal of Chromium and Mercury ions from aqueous solution. J. Nanomater. 2022: 1-15.
17. Elrouby M., Abdel-Mawgoud A. M., El-Rahman R. A., (2017), Synthesis of Iron Oxides nanoparticles with very high saturation magnetization form TEA-Fe(III) complex via electrochemical deposition for supercapacitor applications. J. Mol. Struct. 1147: 84-95.
18. Kheradmand E., Delavari H., Poursalehi R., (2015), The effect of dissolved Oxygen in arc medium on crystal structure and optical properties of Iron based nanoparticles prepared via Dc arc discharge in water. Proc. Mat. Sci. 11: 695-699.
19. Song K., Kim W., Suh C., Shin D., Ko K., Ha K., (2013), Magnetic Iron Oxide nanoparticles prepared by electrical wire explosion for arsenic removal. Powder Technol. 246: 572-574.
20. Lerner M. I., Lozhkomoev A. S., Bakina O., (2016), Synthesis of Al nanoparticles and Al/AlN composite nanoparticles by electrical explosion of aluminum wires in argon and nitrogen. Powder Technol. 295: 307-314.
21. Raffi M., Saba M., Tariq M., Akhter J., Yavar W., Hasan M., (2010), Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Ann. Microbiol. 60: 75-80.
22. Sundaram R., Yamada T., Hata K., Sekiguchi A., (2017), Electrical performance of lightweight CNT-Cu composite wires impacted by surface and internal Cu spatial distribution. Sci. Rep. 7: 1-11.
23. Lee Y. S., Bora B., Yap S. L., Wong C. S., (2012), Effect of ambient air pressure on synthesis of copper and copper oxide nanoparticles by wire explosion process. Curr. App. Phys. 12: 199-203.
24. Park E., Park H. W., Lee J., (2015), Synthesis of hierarchical copper oxide composites prepared via electrical explosion of the wire in liquids method. Colloid. Surf. A. 482: 710-717.
25. Buazar F., Cheshmehkani A., Kassaee M. Z., (2012), Nanosteel synthesis via arc discharge: Media and current effects. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 9: 151-156.
26. Kassaee M., Buazar F., Motamedi E., (2010), Effects of current on arc fabrication of Cu nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2010: 1-5.
27. Horvat R., (2010), Review of antibiogram preparation and susceptibility testing systems. Hosp. Pharm. 45: S6-S9.
28. Seil J. T., Webster T. J., (2012), Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: Methods and literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 7: 2767-2781.
29. Wasfi A. S., Humud H. R., Fadhil N. K., (2019), Synthesis of core-shell Fe3O4-Au nanoparticles by electrical exploding wire technique combined with laser pulse shooting. Opt. Laser Technol. 111: 720-726.
30. Farbod M., Movahed A., Kazeminezhad I., (2012), An investigation of structural phase transformation of monosize γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles fabricated by arc discharge method. Mater. Lett. 89: 140-142.
31. Salamat S., Younesi H., Bahramifar N., (2017), Synthesis of magnetic core–shell Fe3O4@TiO2 nanoparticles from electric arc furnace dust for photocatalytic degradation of steel mill wastewater. RSC Adv. 7: 19391-19405.
32. Taccogna F., (2015), Nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in a plasma by laser ablation in liquid. J. Plasma Phys. 81: 1-12.
33. Faraji M., Poursalehi R., Aliofkhazraei M., (2015), The effect of surfactant on colloidal stability, oxidation and optical properties of Aluminum nanoparticles prepared via Dc arc discharge in water. Proc. Mat. Sci. 11: 684-688.
34. Chernavskii P. A., Peskov N. V., Mugtasimov A. V., Lunin V. V., (2007), Oxidation of metal nanoparticles: Experiment and model. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1: 394-411.
35. Hedberg Y. S., Pradhan S., Cappellini F., Karlsson M.-E., Blomberg E., (2016), Electrochemical surface oxide characteristics of metal nanoparticles (Mn, Cu and Al) and the relation to toxicity. Electrochim Acta. 212: 360-371.
36. Ahmadi S., Fazilati M., Nazem H., Mousavi S. M., (2021), Green synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles using satureja hortensis essential ol toward superior antibacterial/fungal and anticancer performance. BioMed. Res. Int. 2021: 1-9.
37. Xu Q., Feng J., Li L., Xiao Q., Wang J., (2015), Hollow ZnFe2O4/TiO2 composites: High-performance and recyclable visible-light photocatalyst. J. Alloy. Compd. 641: 110-118.
38. Vidhya K., Saravanan M., Bhoopathi G., Devarajan V. P., Subanya S., (2014), Structural and optical characterization of pure and starch-capped ZnO quantum dots and their photocatalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 5: 235-243.
39. Shabgard M. R., Najafabadi A. F., (2014), The influence of dielectric media on nano-structured tungsten carbide (WC) powder synthesized by electro-discharge process. Adv. Powder Technol. 25: 937-945.
40. Karakoti A. S., Munusamy P., Hostetler K., Kodali V., Kuchibhatla S., Orr G., Pounds J. G., Teeguarden J. G., Thrall B. D., Baer D. R., (2012), Preparation and characterization challenges to understanding environmental and biological impacts of nanoparticles. Surf. Interface Anal. 44: 882-889.
41. Predescu A., Matei E., Berbecaru A., Cristian P., Dragan C., Vidu R., Kuncser V., (2018), Synthesis and characterization of dextran-coated Iron Oxide nanoparticles. Roy. Soc. Open Sci. 5: 1-16.
42. Lari L., Steinhauer S., Lazarov V. K., (2020), In situ TEM oxidation study of Fe thin-film transformation to single-crystal magnetite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 55: 12897-12905.
43. Arakha M., Pal S., Devyani S., Tapan K., Bairaji C., Krishna P., Mallick B., Jha S., (2015), Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 5: 1-14.
44. Yusof N. A. A., Zain N. M., Pauzi N., (2019), Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles with chitosan as stabilizing agent and their antibacterial properties against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 124: 1132-1136.
45. Rajabi S. K., Sohrabnezhad S., (2018), Fabrication and characteristic of Fe3O4@MOR@CuO core-shell for investigation antibacterial properties. J. Fluorine Chem. 206: 36-42.
46. Riaz M., Zia R., Saleemi F., Hussain T., (2018), In Vitro antibacterial activity of Ta2O5 doped glass-ceramics against pathogenic bacteria. J. Alloy. Compd. 764: 10-16.
47. Armijo L. M., Wawrzyniec S. J., Kopciuch M., Brandt Y., Rivera A., (2020), Antibacterial activity of iron oxide, iron nitride, and tobramycin conjugated nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J. Nanobiotechnol. 18: 1-27.