We review here key geological heritage elements of the Hațeg Country UNESCO Global Geopark (Southern Carpathians, western Romania) represented by latest Cretaceous continental vertebrate fossils and the sedimentary rocks enclosing them. Based on available geological and paleontological evidence, these animals were living on a tropical island. This paleogeographic setting led to the development of some […]

The transnational Novohrad-Nógrád Geopark situated in Northern Hungary and Southern Slovakia has several important Neogene fossil sites developed for geotourism. One of them is the lower Miocene paleontological locality complex at Ipolytarnóc , which has been well known since the middle of the 19th century. The site is the main geotouristic gateway to the geopark, […]
The Petrified Forest of Lesvos is a Protected Natural Monument showing standing and lying petrified tree trunks, preserved by intense volcanic activity in the early Miocene. The Natural History Museum of Lesvos Petrified Forest contributed significantly to scientific research, conservation, exhibition, promotion and international recognition of the Lesvos Island UNESCO Global Geopark, a founding member […]

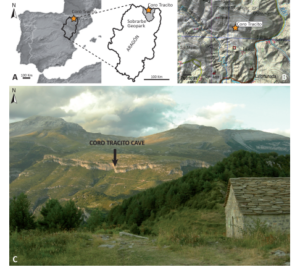
The Sobrarbe-Pirineos UNESCO Global Geopark shows an extremely well-developed underground karst relief as a result of the great abundance and thickness of its limestone formations. The most important Pleistocene vertebrate site within the Geopark is Coro Tracito Cave at Tella. The fossil association is made up exclusively of bones belonging to Ursus spelaeus from the […]