Published in Issue 2015-08-07
How to Cite
Devadiga, A., Shetty, K. V., & Saidutta, M. B. (2015). Timber industry waste-teak (Tectona grandis Linn.) leaf extract mediated synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles. International Nano Letters, 5(4 (December 2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-015-0157-4
HTML views: 12
PDF views: 66
Abstract
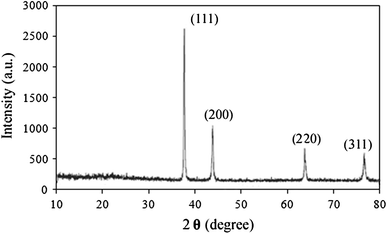
Abstract The current research article emphasizes efficacious use of teak leaves, an agro -biowaste from world’s premier hardwood timber industry, for “green” synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Bioactive compounds of the leaves act as prolific reducing and stabilizing agents in AgNP synthesis. The characterization of the AgNPs synthesized using teak leaves revealed that the particles are spherical with an average size of 28 nm and the presence of bioactive compounds present in teak leaf extract as capping agents on the nanoparticles. A prominent decrease in the content of bioactive compounds such as polyphenols, antioxidants and flavonoids after the biosynthesis of AgNPs signifies that these class of compounds act as reductants and stabilizers during biosynthesis. The biosynthesized silver nanoparticles were also successfully evaluated for their antibacterial characteristics against waterborne pathogens, E. coli and S. aureus, with minimum inhibitory concentration of 25.6 μg/mL. Exploitation of agrowaste resources for synthesis of AgNPs curtails indiscriminate usage of food and commercial plant materials, rather contributing a sustainable way for effective plant waste biomass utilization and management. The biosynthesized AgNps have potential application in water purifiers, antibacterial fabrics, sports wear and in cosmetics as antibacterial agent and the process used for its synthesis being greener is highly beneficial from environmental, energy consumption and economic perspectives.Keywords
- Teak,
- Silver nanoparticles,
- Biosynthesis,
- Timber industry waste,
- Antibacterial property
References
- Rai et al. (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials (pp. 76-83) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002
- Salata (2004) Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-2-3
- Hu et al. (2010) Low temperature sintering of Ag nanoparticles for flexible electronics packaging https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3502604
- Durán et al. (2007) Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles produced by fungal process on textile fabrics and their effluent treatment (pp. 203-208) https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2007.022
- Kokura et al. (2010) Silver nanoparticles as a safe preservative for use in cosmetics (pp. 570-574) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.12.002
- Chau et al. (2005) Microwave plasma synthesis of silver nanopowders (pp. 905-908) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2004.10.068
- Lin et al. (2009) Rapid, solventless, bulk preparation of metal nanoparticle-decorated carbon nanotubes (pp. 871-884) https://doi.org/10.1021/nn8009097
- Pal et al. (2009) Microwave-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ethanol as a reducing agent (pp. 530-532) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.11.056
- Pillai and Kamat (2004) What factors control the size and shape of silver nanoparticles in the citrate ion reduction method? (pp. 945-951) https://doi.org/10.1021/jp037018r
- Panáček et al. (2006) Silver colloid nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity (pp. 16248-16253) https://doi.org/10.1021/jp063826h
- Sun and Xia (2002) Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles (pp. 2176-2179) https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1077229
- Vigneshwaran et al. (2007) Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus flavus (pp. 1413-1418) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.07.042
- Shahverdi et al. (2007) Rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatants of Enterobacteria: a novel biological approach (pp. 919-923) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2007.02.005
- Govindaraju et al. (2009) Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by a marine alga, Sargassum wightii Grevilli and their antibacterial effects (pp. 5497-5501) https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2009.1199
- Christensen et al. (2011) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Murraya koenigii (curry leaf): an investigation on the effect of broth concentration in reduction mechanism and particle size (pp. 429-434) https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2011.4256
- Zargar et al. (2011) Green synthesis and antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles using Vitex Negundo L (pp. 6667-6676) https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16086667
- Shameli et al. (2012) Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Curcuma longa tuber powder (pp. 5603-5610) https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S36786
- Roopan et al. (2013) Low-cost and eco-friendly phyto-synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cocos nucifera coir extract and its larvicidal activity (pp. 631-635) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.08.013
- Vijayakumar et al. (2013) Biosynthesis, characterisation and anti-bacterial effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Artemisia nilagirica (pp. 235-240) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.04.017
- Sathishkumar et al. (2009) Cinnamon zeylanicum bark extract and powder mediated green synthesis of nano-crystalline silver particles and its bactericidal activity (pp. 332-338) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.06.005
- Ankamwar et al. (2005) Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Emblica officinalis fruit extract, their phase transfer and transmetallation in an organic solution (pp. 1665-1671) https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2005.184
- Mukunthan et al. (2011) Catharanthus roseus: a natural source for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles (pp. 270-274) https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60041-5
- Kore, K. J., Pradip, Jadhav, J., Shete, R. V., Shetty, S. C.: Diuretic property of
- Tectona grandis
- leaves aqueous extract in Wistar rats. Inter. J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 3, 141–146 (2011)
- Rao et al. (2011) In-vitro anti-oxidant and free radical scavenging activity of various extracts of Tectona grandis. Linn Leaves (pp. 440-442)
- Purushotham et al. (2010) Synergistic in vitro antibacterial activity of Tectona grandis leaves with tetracycline (pp. 519-523)
- David et al. (2010) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Euphorbia hirta L and their antifungal activities (pp. 76-81)
- Cruz et al. (2010) Preparation and physicochemical characterization of Ag nanoparticles biosynthesized by Lippia citriodora (Lemon Verbena) (pp. 67-73) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.06.025
- Krishnaraj et al. (2010) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens (pp. 50-56) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.10.008
- Singhal et al. (2011) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi) leaf extract and screening its antimicrobial activity (pp. 2981-2988) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0193-y
- Foldbjerg et al. (2011) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in the human lung cancer cell line, A549 (pp. 743-750) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0545-5
- Chew, L., Yik, C., Wan, L., Elaine, T., Ling P., Lim, Y., Yau, G., Kheng, J., Stanlas, J.: Assessment of phytochemical content, polyphenolic composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Leguminosae medicinal plants in Peninsular Malaysia. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 12, 1–1.
- http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/11/12
- (2010)
- Wolfe et al. (2010) Antioxidant activity of apple peels (pp. 609-614) https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020782a
- Ordon-Ez et al. (2006) Antioxidant activities of Sechium edule (Jacq.) Swart extracts (pp. 452-458) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.024
- Adedapo et al. (2008) Evaluation of the medicinal potentials of the methanol extracts of the leaves and stems of Halleria lucida (pp. 4158-4163) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.066
- Benzie and Strain (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of ‘‘antioxidant power’’: the FRAP assay (pp. 70-76) https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0292
- Antibiotic susceptibility testing of aquaculture associated bacteria with the broth macrodilution method (Mic determination) SOP ASIARESIST, Laboratory of Microbiology, K. L. Ledeganckstr. 35, B-9000 Gent (Belgium)
- Basavaraja et al. (2008) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium semitectum (pp. 1164-1170) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2007.06.020
- Rastogi and Arunachalam (2011) Sunlight based irradiation strategy for rapid green synthesis of highly stable silver nanoparticles using aqueous garlic (Allium sativum) extract and their antibacterial potential (pp. 558-563) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.04.068
- Wei et al. (2012) S ynthesis of silver nanoparticles by solar irradiation of cell-free Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracts and AgNO3 (pp. 273-278) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.118
- Dwivedi and Gopal (2010) Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Chenopodium album leaf extract (pp. 27-33) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.07.020
- Sathishkumar et al. (2010) Immobilization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Curcuma longa tuber powder and extract on cotton cloth for bactericidal activity (pp. 7958-7965) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.051
- Khalil et al. (2014) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using olive leaf extract and its antibacterial activity (pp. 1131-1139) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.04.007
- Prathna et al. (2011) Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Citrus limon (lemon) aqueous extract and theoretical prediction of particle size (pp. 152-159) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.08.036
- Ramamurthy, C. H., Padma, M., Samadanam Daisy Mariya I., Mareeswaran, R., Suyavaran, A., Suresh Kumar, M., Premkumar, B.: The extra cellular synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles and their free radical scavenging and antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces. 102, 808–815 (2013)
- Sethuraman and Edison (2012) Instant green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Terminalia chebula fruit extract and evaluation of their catalytic activity on reduction of methylene blue (pp. 1351-1357) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.04.025
- MubarakAli et al. (2011) Plant extract mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens (pp. 360-365) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.03.009
- Nazeruddin et al. (2014) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and its anti-microbial activity (pp. 272-277) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.07.111
- Kim et al. (2011) Antibacterial activity of silver-nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli (pp. 77-85)

 10.1007/s40089-015-0157-4
10.1007/s40089-015-0157-4