Published in Issue 2013-06-27
How to Cite
Maria, K. H., Choudhury, S., & Hakim, M. A. (2013). Structural phase transformation and hysteresis behavior of Cu-Zn ferrites. International Nano Letters, 3(1 (December 2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-3-42
PDF views: 36
HTML views: 5
Abstract
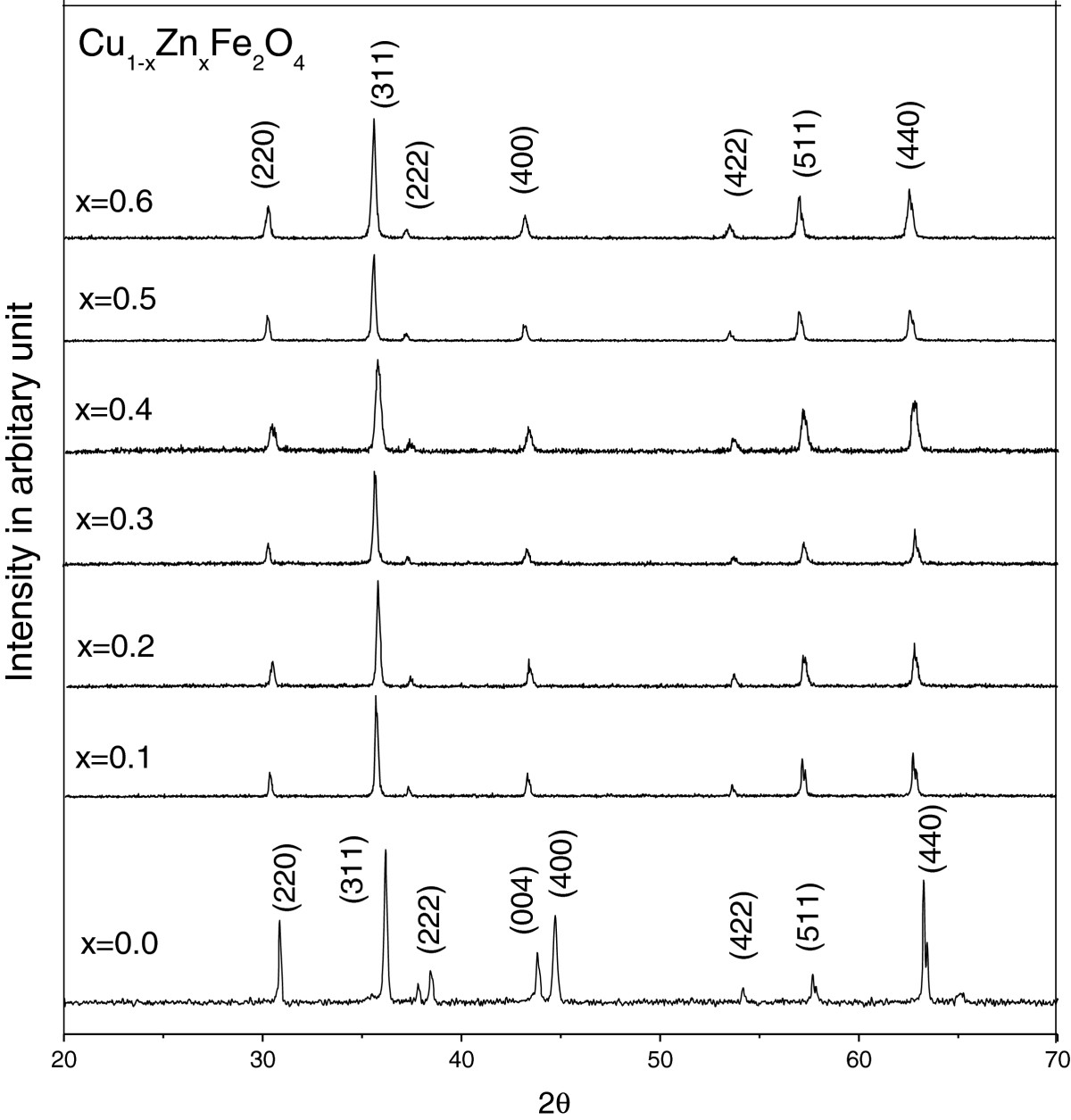
Abstract A series of Cu 1- x Zn x Fe 2 O 4 ferrite (with x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6) compositions were synthesized using the standard solid-state reaction technique. X-ray diffraction was used to study the structure of the above investigated samples. The theoretical and experimental lattice parameters ( a th and a exp ) were calculated for each composition. A significant decrease in density and subsequent increase in porosity were observed with increasing Zn content. Curie temperature, T C , has been determined from the temperature dependence of permeability and found to decrease with increasing Zn content. The anomaly observed in the temperature dependence of permeability was attributed to the existence of two structural phases: cubic phase and tetragonal phase. Low-field hysteresis measurements have been performed using a B - H loop trace from which hysteresis parameters have been determined. Coercivity and hysteresis loss were estimated with different Zn contents.Keywords
- Cu-ferrites,
- Zn-ferrites,
- XRD,
- permeability,
- hysteresis loss,
- coercivity
References
- Goldman (1990) Van Nostrand
- Chen (1990) North-Holland
- Batoo (2011) Structural and electrical properties of Cu doped NiFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared through modified citrate gel method (pp. 1400-1407) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2011.08.005
- Pettit and Forester (1971) Mossbauer study of cobalt-zinc ferrites 4(11) (pp. 3912-3924) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.4.3912
- Kulkarni and Patil (1982) Magnetic ordering in Cu-Zn ferrite (pp. 843-848) https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540382
- Satyamurthy et al. (1969) Yafet-Kittel angles in zinc-nickel ferrites 181(2) (pp. 969-977) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.181.969
- Manjurul Haque et al. (2009) Effect of Zn substitution on the magnetic properties of Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 ferrites (pp. 3915-3921) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2009.07.124
- Dunitz and Orgel (1975) Electronics properties of transition metal oxides—I: distribution from cubic symmetry (pp. 20-29) https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(57)90043-4
- Manjura Hoque et al. (2011) Structural and magnetic properties of Li-Cu mixed spinel ferrites (pp. 1799-1804) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.02.031
- Nelson and Riley (1945) An experimental investigation of extrapolation methods in the derivation of accurate unit cell dimension of crystals (pp. 160-177) https://doi.org/10.1088/0959-5309/57/3/302
- Mazen et al. (1993) X-ray analysis and IR absorption spectra of Li-Ge ferrite (pp. 35-40) https://doi.org/10.1016/0254-0584(93)90116-4
- Smit and Wign (1959) Wiley
- Patange et al. (2009) Cation distribution by Rietveld, spectral and magnetic studies of chromium-substituted nickel ferrites (pp. 429-434) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4897-0
- Ahmed et al. (2005) Structural and electrical studies on Ln3+ substituted Ni-Zn ferrite (pp. 310-321) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.05.049
- Verma et al. (2013) Cation distribution and Mössbauer studies of Mg0.2Mn0.5Ni0.3InxFe2-xO4 ferrites (x = 0.0, 0.05 and 0.10) (pp. 148-153) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.02.101
- Globus et al. (1977) Distance between magnetic ions and fundamental properties in ferrites C1(38) (pp. 163-168)
- Hakim et al. (2013) Cation distribution and electromagnetic properties of spinel type Ni-Cd ferrites (pp. 1316-1321) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2013.04.011
- Vegard (1921) Die Konstitution der Mischkristalle und die Raumfüllung der atome (pp. 17-26) https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01349680
- Batoo and Ansari (2012) Low temperature-fired Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite nanoparticles through auto combustion method for multilayer chip inductor applications (pp. 112-126) https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-112
- Ladgaonker et al. (2001) Cation distribution and magnetization study of Nd3+ substituted Zn-Mg ferrites (pp. 129-135)
- Ladgaonker et al. (2000) Effect of Zn2+ and Nd3+ substitution on magnetisation and AC susceptibility of Mg ferrite (pp. 289-294) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(99)00468-0
- Ravinder and Reddy (2003) Thermoelectric power studies of polycrystalline magnesium substituted lithium ferrites (pp. 127-133) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)01545-7
- Yunus et al. (2001) Neotron diffraction studies of diluted spinel ferrite ZnxMg0.75–x Cu0.25Fe2O4 (pp. 121-132) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)00224-4
- Bellad et al. (1999) Microstructure and permeability studies of mixed Li-Cd ferrites (pp. 57-64) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(98)01073-7
- Mazen et al. (1995) The effect of Ge4+ substitution in lithium ferrites (pp. 685-690) https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.2211490219
- Pandit et al. (2005) Magnetic and dielectric properties of Mg1-xMnxFe2-2xO4 ferrite system (pp. 423-428) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-6099-x
- Muhammad and Maqsood (2008) Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Cu1-xZnxFe2O4 ferrites (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) (pp. 54-59) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.06.019
- Abbas et al. (1995) Study of sintering behavior and electrical properties of Cu-Zn-Fe-O system (pp. 1419-1426) https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984995001418
- Verma et al. (2005) Temperature dependence of electrical properties of nickel-zinc ferrites processed by the citrate precursor technique (pp. 1-6) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2004.08.011
- Xiwei et al. (2002) Effect of Mn substitution on the magnetic properties of MgCuZn ferrites (pp. 316-322) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00854-5
- Neel (1948) Magnetic properties of ferrites: ferrimagnetism and antiferromagnetism (pp. 137-198)
- Globus and Duplex (1966) Separation of susceptibility mechanisms for ferrite of low anisotropy 2(3) (pp. 441-445) https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.1966.1065867
- Dawoud and Shaat (2006) Initial permeability and DC conductivity of Cu-Zn ferrite (pp. 165-182)
- Bergestain and Cervinka (1961) Influence of manganese and oxygen content on the tetragonal deformation of copper ferrite (pp. 584-594) https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01689155
- Bleaney and Bleaney (1976) Oxford University Press
- Jahan et al. (1937) Stability of polyatomic molecules in degenerate electronic states. I. Orbital degeneracy (pp. 220-235) https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1937.0142
- Mazen and Dawoud (1999) Structure and magnetic properties of Li-Cu ferrite (pp. 275-289) https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-396X(199904)172:2<275::AID-PSSA275>3.0.CO;2-H
- Maria et al. (2011) Influence of Zn substitution on the Curie temperature and transport properties of Cu ferrite 3(1) (pp. 23-32)
- Valenzula (1980) A sensitive method for the determination of the Curie temperature in ferrimagnets (pp. 3173-3174) https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00550394
- Maria et al. (2010) Magnetic properties of Zn substituted copper ferrites (pp. 105-108)
- Xu (2003) Magnetic anisotropy and Mossbauer spectra in disordered lithium-zinc ferrites (pp. 4746-4749) https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1562745
- Nath et al. (2012) Magnetic ordering in Ni-Cd ferrite (pp. 2116-2120) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.023
- Noor et al. (2012) Magnetic behavior of Cd2+ substituted cobalt ferrites (pp. 227-231) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2011.10.038
- Akhter and Hakim (2010) Magnetic properties of cadmium substituted lithium ferrites (pp. 399-403) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.11.023
- Gonchar et al. (2003) Problems of increasing of thermostability of high permeable Ni-Zn ferrites and relative materials for telecommunications (pp. 544-546) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00860-0
- Patil et al. (1993) Conduction mechanism in Sn4+ substituted copper ferrite (pp. 267-271) https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02746036
- Hankare et al. (2010) Effect of zinc substitution on structural and magnetic properties of copper ferrite (pp. 37-41) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.03.178
- Coey (1996) Wiley
- Jain et al. (1976) Effect of intragranular porosity of initial permeability and coercive force in a manganese zinc ferrite (pp. 1335-1338) https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545155
- Nam et al. (1997) The effect of Mn substitution on the properties of NiCuZn ferrites (pp. 4794-4796) https://doi.org/10.1063/1.365466

 10.1186/2228-5326-3-42
10.1186/2228-5326-3-42