Vermicomposting: A technology for vermiremediation of heavy metals from sewage sludge and animal dung
- Department of Zoology, Government Degree College, Dhadha Bujurg, Hata, Kushinagar-274207, U.P., India
- Department of Zoology, S.V.M. Mahila, P.G. College, Gorakhpur-273001, U.P., India
- Vermibiotechnology Laboratory, Department of Zoology, D.D.U. Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur, 273009, U.P., India

Received: 2023-04-12
Revised: 2023-08-11
Accepted: 2024-05-22
Published in Issue 2024-05-20
Copyright (c) 2024 @Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
PDF views: 497
HTML views: 34
Abstract
Purpose: The present study to investigate the earthworm Eisenia fetida was a chief organism for accumulation of heavy metals (Pb, Cr, and Cd) in their body tissue from sewage sludge with different combinations of animal dung and converted into rich organic vermicompost which plays a beneficial role for environment, animals and human health.
Method: Animal dung and sewage sludge were collected from Gorakhpur city and earthworm E. fetida an epigeic species collected from Vermibiotechnology Laboratory, Department of Zoology, D. D. U. Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur. Analysis of heavy metals in different animal dung, sewage sludge, final vermicompost, and earthworm bodies were measured by Shimadzu AA-7000 atomic absorption spectrometer.
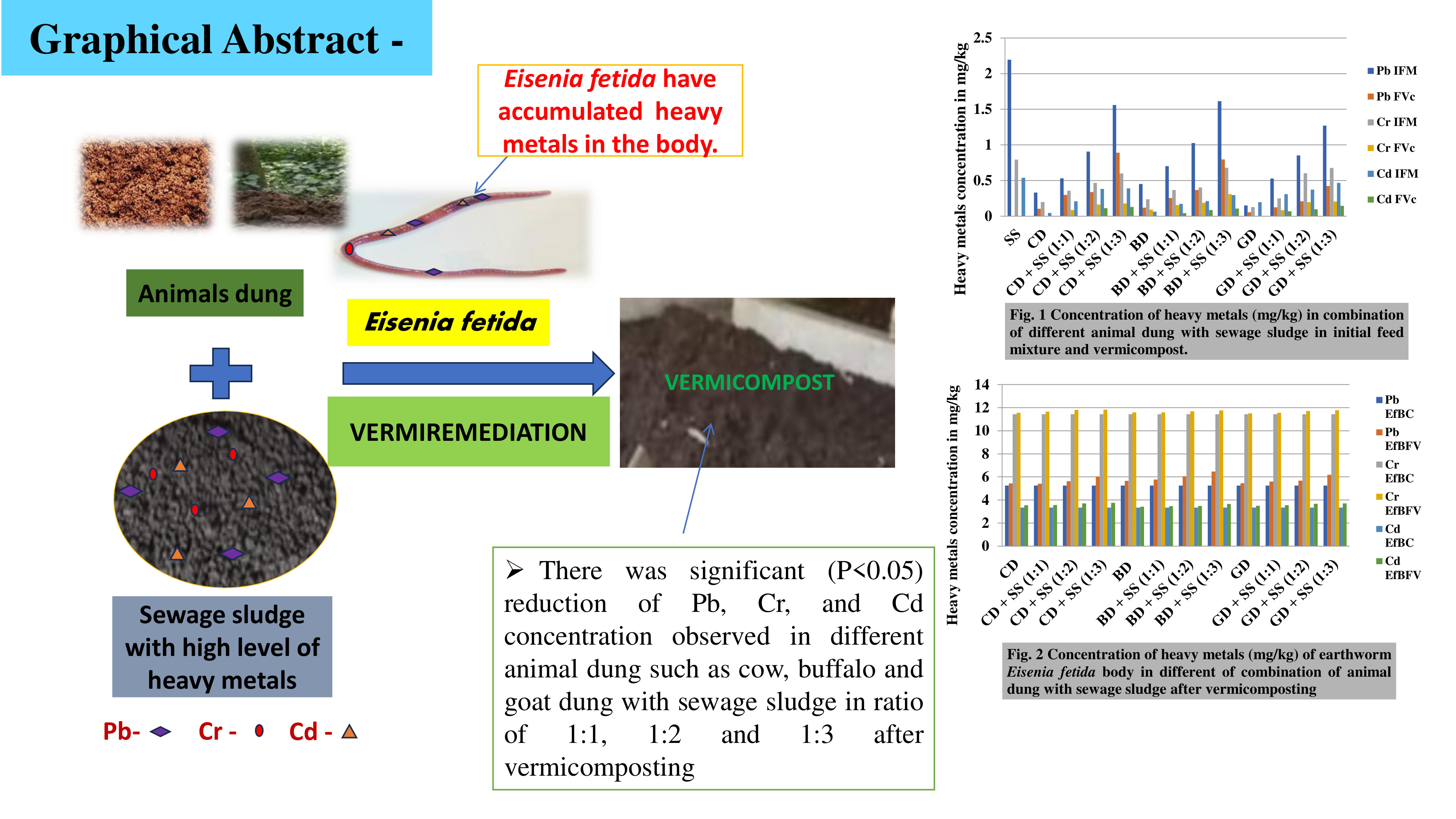
Results: There was a significant (P<0.05) reduction of Pb, Cr, and Cd concentration observed in different animal dung such as cow, buffalo and goat dung with sewage sludge in ratios of 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3 before and after vermicomposting. Cr was significantly decreased in cow dung (CD) and goat dung (GD) and Cd in cow dung (CD) and cow dung with sewage sludge (CD+SS, 1:1) the at BDL level whereas the concentration of Pb significantly decreased by 76.470% in the combination of GD+SS (1:1). The Cr and Cd were significantly increased in the body of E. fetida 3.384% and 11.801%, respectively, in the combination of CD+SS (1:3) whereas Pb significantly increase by 23.018% in the combination of BD+SS (1:3).
Conclusion: E. fetida is a suitable species for the accumulation of heavy metals such as Pb, Cr, and Cd in different vermibeds during vermicomposting and plays an important role in the remediation of heavy metals from animal dung with sewage sludge. Vermibiotechnology is a useful technique for the management of heavy metals.
Research Highlights
- Vermicomposting has a great potency to process a wide range of wastes produced in agriculture, animal wastes, sewage sludge management, and generate high-quality end products, i.e., vermicompost that can have agricultural uses.
- Vermicomposting involves the “cooperation” between earthworms and microorganisms during a biological process.
- fetida accumulated heavy metals in the body from biological wastes during vermicomposting.
- It is a useful vermiremediation technique for the management of toxic metals from sewage sludge and protects human health and the environment.
Keywords
- Eisenia fetida,
- Heavy metals,
- Sewage sludge,
- Vermicomposting,
- Vermiremediation

 10.57647/ijrowa-3kgw-nr28
10.57647/ijrowa-3kgw-nr28